Simulating potential effects of climatic warming on altitudinal patterns of key species in Mediterranean-alpine ecosystems
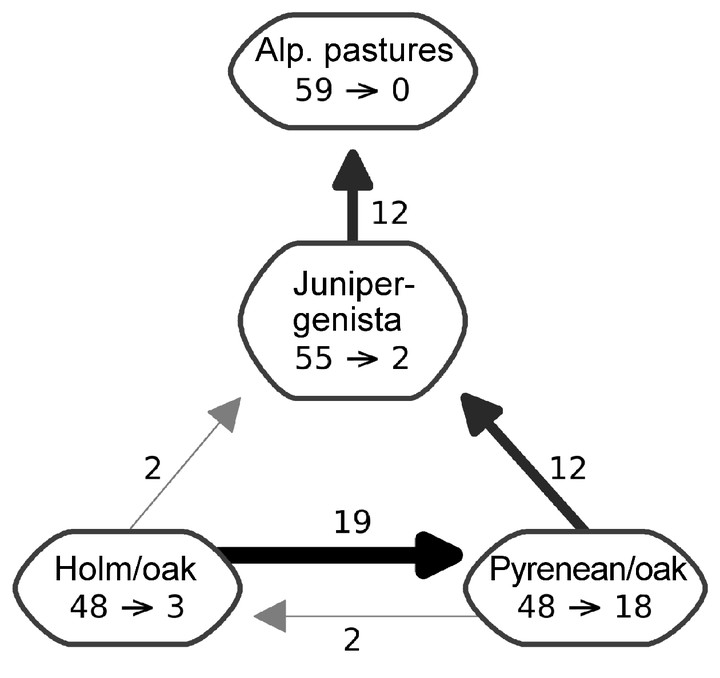 Image credit: Blas M. Benito
Image credit: Blas M. Benito
Abstract
In this paper we study an isolated high-mountain (Sierra Nevada, SE Iberian Peninsula) to identify the potential trends in the habitat-suitability of five key species (i.e. species that domain a given vegetation type and drive the conditions for appearance of many other species) corresponding to four vegetation types occupying different altitudinal belts, that might result from a sudden climatic shift. We used topographical variables and downscaled climate warming simulations to build a high-resolution spatial database (10 m) according to four different climate warming scenarios for the twenty-first century. The spatial changes in the suitable habitat were simulated using a species distribution model, in order to analyze altitudinal shifts and potential habitat loss of the key species. Thus, the advance and receding fronts of known occurrence locations were computed by introducing a new concept named differential suitability, and potential patterns of substitution among the key species were established. The average mean temperature trend show an increase of 4.8°C, which will induce the vertical shift of the suitable habitat for all the five key species considered at an average rate of 11.57 m/year. According to the simulations, the suitable habitat for the key species inhabiting the summit area, where most of the endemic and/or rare species are located, may disappear before the middle of the century. The other key species considered show moderate to drastic suitable habitat loss depending on the considered scenario. Climate warming should provoke a strong substitution dynamics between species, increasing spatial competition between both of them. In this study, we introduce the application of differential suitability concept into the analysis of potential impact of climate change, forest management and environmental monitoring, and discuss the limitations and uncertainties of these simulations.